What Are Chatbots and Why Are They So Popular?
Chatbots have become increasingly prevalent as AI takes over customer service, reshaping how businesses connect with their customers and providing instant, seamless communication at any time of day. Chatbots are automated systems capable of handling a range of interactions that mimic human conversation. These bots can answer questions, assist with troubleshooting, manage bookings, and even provide product recommendations, often within the environments we’re already using—like websites, messaging platforms, and mobile apps.
Why are chatbots so popular? In a fast-paced world where convenience is key, chatbots offer companies the ability to serve customers instantly, 24/7, without requiring live agents. They are particularly valuable for high-demand tasks that benefit from quick responses, such as order status updates, FAQs, or directing customers to resources. It’s no surprise that nearly 40% of internet users worldwide now prefer to interact with chatbots for simple tasks. Chatbots are accessible, efficient, and create new ways for companies to deliver quality service, creating strong customer relationships through timely engagement.
Understanding What Chatbots Are and How They Work
Defining Chatbots in Simple Terms
A chatbot, at its core, is a program that simulates human conversation using pre-programmed responses or artificial intelligence (AI). These bots are designed to understand language inputs, analyze them, and respond appropriately based on the context. Chatbots vary in complexity, from simple rule-based systems that respond to specific triggers to advanced AI-powered bots that can understand natural language and even learn from past interactions.
In essence, chatbots act as virtual assistants. They can take on various forms: a live chat widget on a website, a voice assistant in a mobile app, or even an automated text message thread. By understanding user inputs and responding accordingly, chatbots provide a seamless interaction that feels conversational, helping users solve issues, find information, or complete transactions with ease.
A Brief History and Evolution of Chatbots
The history of chatbots goes back further than many people might realize. The first notable example of a chatbot was ELIZA, created in the 1960s by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum. ELIZA was a simple bot that simulated conversation by using pattern-matching techniques and scripts to respond to user inputs. Although rudimentary, it sparked the early interest in developing machines that could engage in human-like conversations.
Over the following decades, chatbots evolved, with each new iteration pushing the boundaries of what conversational technology could do. In the 1990s, a more advanced chatbot named A.L.I.C.E. (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) was developed, using natural language processing techniques to engage in conversations. Then, in 2001, SmarterChild emerged as a playful, helpful bot on AOL Instant Messenger, giving users weather updates, sports scores, and more.
The modern chatbot landscape transformed significantly with the advancement of AI and machine learning in the 2010s. With these technologies, chatbots moved from simple responses to truly interactive experiences, capable of learning from data and understanding context in conversations. Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are some of the most sophisticated examples of today’s AI-driven bots, capable of handling a vast range of tasks from making calls to providing real-time information on a variety of topics.
Types of Chatbots: Rule-Based vs. AI-Driven
There are two primary types of chatbots: rule-based and AI-driven. Each has a distinct purpose and level of sophistication, and understanding the difference can clarify why some bots feel more limited in scope while others seem to grasp complex requests.
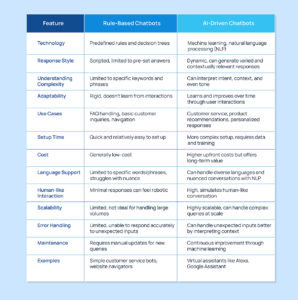
Rule-Based Chatbots
Rule-based chatbots operate on a series of predefined commands or rules. They’re programmed to recognize specific words or phrases and respond accordingly. For instance, if a user types “What are your hours?” a rule-based bot would match that phrase with a pre-set answer like “Our hours are 9 AM to 5 PM.” These bots are best for straightforward queries where predictable responses are sufficient, like answering FAQs or providing simple information.
However, rule-based bots are limited by their programming. They can’t understand variations in language or handle requests outside their scripts, which can sometimes lead to frustration if the bot doesn’t understand what a user is asking. Despite these limitations, rule-based bots are efficient, cost-effective, and perfect for businesses looking for basic automation.
AI-Driven Chatbots
AI-driven chatbots, often referred to as “smart bots” or “conversational AI,” use machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to language in a way that’s closer to human interaction. Unlike rule-based bots, they can analyze the intent behind words, recognize complex language patterns, and even learn from previous conversations to improve over time.
For example, if a user says, “I need help with my order,” an AI-driven bot can understand that the user has an order-related question and respond with options or further prompts. Over time, these bots can even anticipate common issues and offer proactive solutions based on previous user behavior and interactions.
AI-driven chatbots are increasingly popular in customer service, healthcare, and e-commerce due to their ability to provide tailored assistance and handle a wide variety of inquiries. As they improve, they’re becoming capable of engaging in highly personalized conversations, making users feel understood and valued.
How Do Chatbots Work? A Look Behind the Scenes

The functionality of chatbots varies depending on their type, but generally, all chatbots follow a similar process for interpreting and responding to user input. Here’s a closer look at the mechanisms behind how chatbots work:
Processing User Input through NLP
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is a foundational technology for most chatbots, allowing them to interpret human language, whether written or spoken. When a user inputs a message, NLP algorithms break down the language into elements the chatbot can understand. This process involves identifying key phrases, detecting user intent, and extracting relevant information. For instance, if a user types, “What’s the status of my order?” NLP helps the chatbot understand that this is a question related to order tracking.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): NLU is a subset of NLP that interprets the intent and meaning behind the text, enabling the chatbot to provide accurate responses. This is particularly crucial for AI-driven chatbots, which rely on NLU to handle complex conversations where context is key.
Using Algorithms to Generate Responses
Response Generation: Once the chatbot has identified the user’s intent, it selects an appropriate response based on its programming or learned patterns. Rule-based bots rely on decision trees, matching keywords with predefined responses. For AI-driven chatbots, response generation is more dynamic. They use complex algorithms to analyze past interactions, predict responses, or even generate new responses based on user input.
Conversational Flow: A smooth conversational flow is essential for user satisfaction. Advanced bots use algorithms to anticipate follow-up questions and guide users through tasks. For example, if a user initiates a conversation about ordering a product, the chatbot might follow up with questions like “What size do you need?” or “Would you like to see related items?”
Machine Learning and Training
Training and Learning: AI chatbots improve over time through machine learning, which allows them to learn from user interactions and adapt their responses. Training typically involves feeding the bot with a dataset of common queries and responses. With supervised learning, chatbots can adjust their responses based on real conversations, enhancing accuracy.
Personalization: Machine learning also enables chatbots to tailor responses to individual users, improving the interaction experience. For example, if a chatbot learns that a customer frequently asks about shipping details, it may prioritize shipping information in future interactions.
Feedback Loop and Continuous Improvement
Feedback and Iteration: Many advanced chatbots incorporate a feedback loop, allowing users to rate their interactions or provide comments. This feedback is valuable for fine-tuning the chatbot’s performance and ensuring it meets user expectations.
Iterative Learning: Continuous learning allows chatbots to improve based on user interactions, industry trends, and new data. The more a chatbot engages with users, the more refined its responses become, making it more efficient over time.
The Benefits of Chatbots: Why Businesses Are Adopting Them
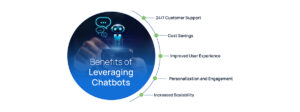
Chatbots are transforming business operations across various industries, bringing a host of benefits that improve efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Here are some of the key advantages:
24/7 Customer Support
One of the most significant advantages of chatbots is their ability to provide round-the-clock customer support. Unlike human agents who require breaks and work limited hours, chatbots can engage with users at any time, offering instant responses to common queries.
Example: In the eCommerce sector, chatbots help customers track orders, request refunds, and check product availability even outside regular business hours, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction.
Cost Savings
Chatbots can significantly reduce labor costs by automating high-volume, repetitive tasks, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. This is especially beneficial for small businesses or startups that need to maximize resources.
Example: In the banking industry, many banks use chatbots to automate tasks such as balance inquiries, transaction histories, and payment reminders. By automating these processes, banks save time and money while maintaining service quality.
Improved User Experience
With chatbots, customers can get quick, accurate answers to their questions without navigating long wait times or complex phone menus. By offering seamless, user-friendly interactions, chatbots make the experience more enjoyable and efficient for customers.
Example: Airlines and travel agencies use chatbots to help travelers find flights, make reservations, and check flight statuses. This streamlined support reduces frustration and improves the overall travel experience.
Personalization and Engagement
AI-powered chatbots can use data from past interactions to provide a more personalized experience. For instance, they can recommend products based on previous purchases or tailor responses based on the user’s preferences and history.
Example: In retail, chatbots assist shoppers by recommending products, offering discounts, or personalizing responses, which not only enhances the shopping experience but also boosts conversion rates.
Increased Scalability
Unlike human teams, which require additional hires to handle larger volumes, chatbots can scale effortlessly to meet demand. Whether it’s managing seasonal surges or high-traffic events, chatbots handle increased volumes with ease, making them a reliable solution for businesses that experience fluctuating demand.
Example: During Black Friday or holiday sales, eCommerce websites rely on chatbots to handle the surge in inquiries, providing consistent service without the need to increase staff.
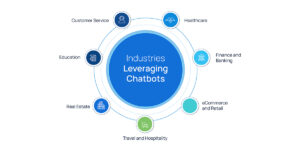
How Different Industries Are Leveraging Chatbots
Chatbots have found applications across diverse sectors, each utilizing them to meet unique business needs and improve customer experience. Here’s a closer look at how chatbots are used in various industries:
Customer Service
Use Case: Many companies, especially those with a high volume of customer inquiries, use chatbots to handle routine questions and troubleshoot issues. Chatbots can handle tasks such as answering FAQs, helping with product recommendations, or directing users to relevant resources.
Example: H&M, the global fashion retailer, uses chatbots to assist customers with product recommendations based on style preferences, helping users browse products and streamline the shopping experience.
Healthcare
Use Case: In healthcare, chatbots assist with patient inquiries, appointment scheduling, symptom checking, and health advice. They also offer reminders for medications or upcoming appointments, ensuring patients stay on top of their care.
Example: Babylon Health, a digital healthcare service, uses AI chatbots to perform preliminary symptom checks. Patients can describe their symptoms to the bot, which then provides advice or directs them to a healthcare provider if needed.
Finance and Banking
Use Case: Chatbots in finance streamline banking by answering questions about accounts, assisting with basic transactions, providing account balance information, and even supporting fraud prevention.
Example: Bank of America’s chatbot, Erica, allows customers to manage accounts, monitor spending, transfer funds, and receive proactive financial tips, enhancing user experience and promoting financial literacy.
eCommerce and Retail
Use Case: In eCommerce, chatbots enhance the shopping experience by helping users find products, offering customer support, processing orders, and providing personalized recommendations.
Example: Sephora, a global beauty retailer, uses a chatbot to offer personalized makeup tips, product recommendations, and a virtual try-on feature. The chatbot’s interactivity has boosted customer engagement and sales.
Travel and Hospitality
Use Case: Travel and hospitality chatbots handle reservations, answer queries, assist with itinerary management, and provide recommendations for local activities, making travel planning easier and more enjoyable for customers.
Example: KLM Royal Dutch Airlines uses a chatbot to assist customers with booking flights, providing travel information, and sending boarding passes, enabling passengers to receive personalized support without waiting.
Real Estate
Use Case: Real estate companies use chatbots to answer inquiries about property listings, schedule viewings, qualify leads, and even assist with mortgage calculators, making the home-buying process smoother.
Example: Apartment Ocean is a real estate chatbot platform that helps agents manage leads, answer questions about properties, and schedule tours, allowing real estate agents to focus on closing deals while the chatbot handles initial inquiries.
Education
Use Case: In education, chatbots can assist students with enrollment, class schedules, and general information. They also serve as study assistants, offering quizzes, reminders, and access to course resources.
Example: Duolingo, a popular language-learning app, uses chatbots to help users practice language skills in real-time, simulating conversational practice and allowing learners to build confidence in a low-pressure setting.
Challenges and Limitations of Chatbots: What Still Needs Improvement?
While chatbots offer immense benefits, they come with their own set of challenges and limitations that can impact user experience and overall effectiveness. Here are some common challenges chatbots face today, along with potential improvements that could address these issues.
Language Understanding and Nuance
Challenge: Chatbots, especially rule-based ones, struggle to fully understand complex language and respond accurately. Subtle nuances, idioms, slang, or specific terminology can easily confuse bots, leading to inaccurate or irrelevant responses.
Improvement: Advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning are helping chatbots become better at understanding the intricacies of human language. Future chatbots will likely be able to interpret these nuances more accurately, making conversations feel more natural.
Lack of Emotional Intelligence and Human Touch
Challenge: While AI-driven chatbots can simulate human-like interactions, they lack genuine empathy and the ability to respond emotionally. For customer service, this lack of emotional intelligence can sometimes lead to frustration, especially when dealing with sensitive or complex issues.
Improvement: Integrating sentiment analysis technology may help chatbots better understand users’ emotions and tailor responses accordingly. The future may also see chatbots that can seamlessly transition users to a human agent when an empathetic response is required.
Handling Complex and Unstructured Queries
Challenge: Chatbots can excel at routine inquiries but often struggle with complex or unstructured questions that require deeper understanding or specialized knowledge. This can be a limitation for industries that deal with technical questions, personalized support, or unique circumstances.
Improvement: AI-driven chatbots are gradually improving at handling complex queries by learning from previous interactions and analyzing similar responses. In the future, they may incorporate specialized knowledge databases or escalate to human support when the query exceeds their capabilities.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Challenge: For many businesses, integrating chatbots with existing systems (like CRMs or ERPs) can be difficult and expensive. Chatbots may be limited in functionality if they can’t fully access and interact with the organization’s data.
Improvement: Emerging chatbot platforms focus on easier integration and compatibility with third-party systems. Future chatbots will likely support more seamless integration across multiple platforms, allowing them to access relevant data more effectively and offer better service.
The Future of Chatbots: What’s Next for Conversational AI?
The future of chatbots is filled with exciting possibilities as technology continues to evolve. Here are some emerging trends and advancements likely to shape the chatbot landscape in the coming years:
Conversational AI and Enhanced NLP
Chatbots are expected to become even more intelligent and conversational with advancements in conversational AI. Enhanced natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning models, like OpenAI’s GPT models, will allow chatbots to interpret user intent and respond in ways that are increasingly accurate and nuanced, creating smoother, more human-like conversations.
Multimodal Chatbots
The next generation of chatbots will likely be multimodal, meaning they can handle not only text and voice but also images, videos, and possibly even augmented reality. This allows chatbots to understand and respond to more types of inputs, making them more versatile and useful for customer support, education, and entertainment.
Example: In eCommerce, a multimodal chatbot could analyze an uploaded photo of a product and provide information on similar items available, or in healthcare, it could process a photo of a rash and offer preliminary advice.
Improved Personalization through Data and AI
Chatbots of the future will leverage AI to offer hyper-personalized experiences, using data to tailor responses, recommend products, and even remember user preferences. By gathering insights from past interactions, chatbots will create more customized experiences that feel unique to each user.
Example: A chatbot in a fitness app could learn a user’s workout habits, suggest personalized routines, and provide motivational reminders based on the user’s goals.
Enhanced Omnichannel Capabilities
Chatbots will increasingly function across multiple channels seamlessly, allowing users to continue conversations across various platforms—websites, social media, and mobile apps—without losing context. This will provide a more cohesive customer experience.
Example: A user might start a conversation with a chatbot on a website and continue it later on a mobile app without repeating their inquiry.
Proactive Customer Engagement
Rather than waiting for users to initiate conversations, future chatbots will engage customers proactively by predicting needs and offering solutions before they’re asked. This shift will make chatbots valuable for customer retention and engagement.
Example: In banking, a chatbot could notify a user if their account balance is low and offer budgeting tips, or in eCommerce, it could suggest relevant products based on past purchases.
The future of chatbots is bright, with innovations focusing on making them smarter, more capable, and more versatile. As AI technology advances, chatbots will play an increasingly central role in providing personalized and meaningful customer experiences across industries.
Conclusion
Chatbots have evolved from simple rule-based systems into powerful AI-driven tools that are transforming customer service, healthcare, finance, eCommerce, and beyond. While they bring numerous benefits—such as 24/7 support, cost savings, and improved user experience—they still face challenges in areas like language understanding, emotional intelligence, and privacy.
As Conversational AI continues to advance, chatbots are poised to become even more versatile and user-friendly, supporting multimodal interactions, personalized experiences, and seamless omnichannel engagement. The future of chatbots holds great potential, promising more intelligent and engaging experiences that will reshape how businesses interact with customers. Chatbots are becoming indispensable, empowering businesses to connect with customers in faster, smarter, and more meaningful ways.
Skit.ai: A leader in Conversational AI for the Accounts Receivable Management Industry
At Skit.ai, we are dedicated to transforming accounts receivables and contact center operations across the globe. Founded in 2016, our mission is to revolutionize customer service interactions with our advanced Conversational AI technology, empowering organizations worldwide.
Recognizing the evolving landscape of customer interactions, we expanded our offerings to include a suite of multichannel AI solutions. This strategic expansion enables seamless, multilingual, and personalized interactions across voice, voicemail, chat, email, and text. Today, Skit.ai is a leader in Conversational AI, driving innovation and setting new standards for customer engagement. Our platform ensures that consumers, regardless of demographic differences, can engage with businesses through their preferred channels.
Our platform is preset with all applicable compliance filters at both federal and state levels, ensuring outreach times and frequencies are fully compliant. Skit.ai complies with TCPA, FDCPA, and Reg F, along with data security standards and certifications such as PCI DSS, SOC II, and HIPAA, guaranteeing data security and privacy.


Skit.ai is not just a leader in Conversational AI; we are innovators committed to empowering businesses with advanced AI technologies. By simplifying consumer interactions and reaching users through their chosen communication channels, we help businesses achieve better results and improve their operations. As we continue to evolve, we remain dedicated to driving success for our clients and setting new standards in the industry.


